What is Urticaria?
Urticaria, also called nettle-rash or hives or wheals in a common language, simply means itching with a rash. Medically, urticaria may be defined as a skin eruption that is allergic (or non-allergic) in origin and is characterized by profound itching, red circular or irregularly shaped eruptions on any part of the body.
Urticaria is commonly misspelled as uticaria, utricaria, urticara, or uricaria. Urticaria is called pitti in Hindi.
Urticaria is an allergic or non-allergic immunological disease, shown on the skin. Characteristically, the skin eruptions are erythematous, raised above the skin level, with intense itching, and usually worsened by itching with slight local warmth. It can be acute or chronic, largely having a tendency to recur frequently for many months or years.
.jpg)
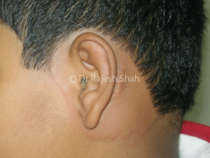
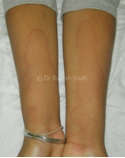
These eruptions can remain on the body for a variable period anywhere between a few seconds and even hours. They have a tendency to disappear and reappear. They tend to disappear without leaving behind any trace.
Location and duration: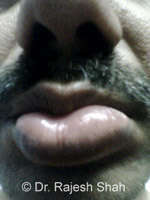
Well, urticaria may appear on any part of the skin. Angioedema is a condition when deep tissues are affected. The typical lesions may last for one minute to half an hour. Some may last even longer. Some patients may get the eruptions once in a while, and some may have them many times during the day. It may be restricted to a couple of spots in some patients, while others may have widespread rashes appearing for days or even months together.
There are acute, sub-acute, chronic, and recurring variants as far as the frequency and duration are concerned.
Histopathological view:
Under the microscope, a typical urticarial rash may exhibit perivascular, cellular infiltrate consisting of lymphocytes and eosinophils, which is indicative of its allergic behavior. There are findings related to edema (swelling) and mucosal inflammation.
Urticaria: The Inner war:
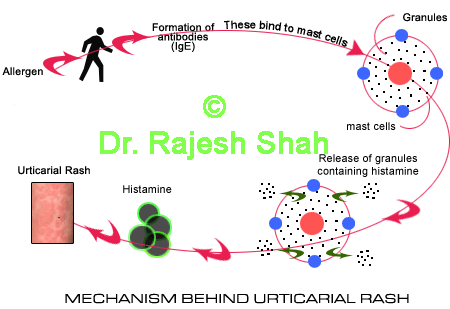 The urticaria rash is a symptom of an allergic and immunological event taking place at the dermal level. The exact understanding is elusive to an extent. In brief, urticaria is a hypersensitive reaction due to the histamine release. The histamine release could be from the mast cells when antigens and antibodies (IgM or IgG) combine to activate the immunological reaction. The histamine release could be IgE-induced. There are certain drugs, pharmacological agents (e.g.: antibiotics, morphine, aspirin, etc.), and food articles (proteins, milk products, etc.) Urticaria is a sign of antigen-antibody reaction. During this process of antibody-antigen reaction, histamine and/or acetylcholine is generated, which has the property of causing vessel dilatation (vasodilation) swelling, itching, pain, and rash.
The urticaria rash is a symptom of an allergic and immunological event taking place at the dermal level. The exact understanding is elusive to an extent. In brief, urticaria is a hypersensitive reaction due to the histamine release. The histamine release could be from the mast cells when antigens and antibodies (IgM or IgG) combine to activate the immunological reaction. The histamine release could be IgE-induced. There are certain drugs, pharmacological agents (e.g.: antibiotics, morphine, aspirin, etc.), and food articles (proteins, milk products, etc.) Urticaria is a sign of antigen-antibody reaction. During this process of antibody-antigen reaction, histamine and/or acetylcholine is generated, which has the property of causing vessel dilatation (vasodilation) swelling, itching, pain, and rash.
Similarly, the treatment also should be targeted towards correcting the internal, immunological derangement by using the medicines which could potentially alter the immune status of the patient. Homeopathy is expected to work with such an approach.
Written & Approved by-
Dr. Rajesh Shah
M.D. (Hom.)