Causes of Urticaria (Hives)
Like many other disease conditions, we know what happens in urticaria more than what exactly causes urticaria (hives). In almost half the cases, we know what causes or induces urticaria, and half the time, the patients or we have no clue as to its exact cause.
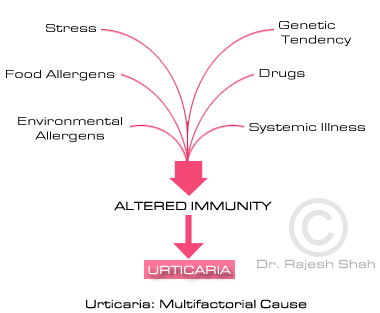
Many people, including some doctors, believe that urticaria is allergic in nature. Actually, it must be noted that Urticaria is not always allergic in nature. There are allergic and non-allergic causes of chronic urticaria. The non-allergic causes include auto-immunity-related, hormonally triggered, stress-triggered, exercise, drugs, temperature-based, and other factors. We shall try to examine some of the most common exciting factors known to induce urticaria (hives), which may be grouped as:
 Allergens: A large number of allergens have been identified as causative agents for some cases of urticaria. It may be noted that urticaria is an individual hypersensitivity and the following factors may not cause urticaria in all urticaria-prone individuals.
Allergens: A large number of allergens have been identified as causative agents for some cases of urticaria. It may be noted that urticaria is an individual hypersensitivity and the following factors may not cause urticaria in all urticaria-prone individuals.
Food allergens: Milk, cheese, eggs, protein products, wheat, cereals, nuts, certain daals as used in India, peas, oranges, fish, chicken, etc. Synthetic and natural food additives and artificially-flavored food articles.
Alcohol:
True anaphylactic reactions to alcohol (ethanol) are rare, and most reactions ingested in alcoholic beverages are secondary to other chemicals in the beverage, such as metabisulfite, papain, dyes, or yeasts. However, there are reports of true allergic reactions in which the offending agent was shown to be the ethanol itself. Generally, the symptoms of anaphylaxis occur in such patients following the ingestion of beer and/or wine. Urticaria rashes have been reported with ethanol ingestion, and hives on contact with ethanol have also been reported for some patients with urticaria.
Environmental factors:
Exposure to pollen, house-dust, buffalo dander, fungi, change in temperature, etc. is known as exciting factors. Extreme cold, heat, and pressure may also induce urticaria.
Drugs, medicines:
The major cause of urticaria is man-made drugs such as antibiotics (Penicillin), NSAIDs, anti-inflammatory drugs (aspirin, indomethacin), vaccinations, foreign sera, hormonal preparations, contraceptive pills, etc. Animals treated with penicillin excrete a small amount of it in the milk sufficient to cause urticaria in sensitive individuals.
Cholinergic factors:
Urticaria often gets triggered or aggravated by exercise, pressure on some part of the body, as well as a change in temperature of the body after sweating. Such changes affect the nerve ending of the skin, which leads to the development of urticarial rash. In this variety of urticaria one experiences itching, burning, and local heat on the skin.
Cocaine:
There have been reports of morphine-induced hives in some people. Bronchospasm may occur in some patients who smoke cocaine or in those who inject heroin. This may occur more often in patients who have a previous history of asthma. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis to cocaine has also been described and is associated with elevated levels of IgE.
Infections and infestations:
Insect bites, Fungal, protozoal, frequent bacterial infections (Urinary tract), viral infections (Hepatitis), helminthiasis (worm infestations such as roundworms, tapeworms), etc. are factors known to cause urticaria. Domestic contact with pet animals should be examined as the cause of urticaria.
Synthetic products:
The use of personal products such as deodorant, perfume, talcum powder, cosmetic products, animal derivatives, and similar synthetic substances may induce this disorder.
 Emotional factors:
Emotional factors:
Especially in chronic, recurring cases of urticaria, the role of emotional factors must be examined. Emotional stresses may directly or indirectly make one susceptible to developing a tendency to urticaria. The psychological factors may work as exciting, aggravating, or maintaining cause. Especially if you are under prolonged stress, anxiety, sadness, or insecurity, such intense emotions could alter your immunological state and in turn lead to hypersensitivity.
Autoimmune causes:
Chronic urticaria is now understood to have an autoimmune link. Presence of autoantibodies against Immunoglobulin E (IgE), CD23 (FcεRII or Fc epsilon RII), which releases histamine, hence leading to chronic urticaria.
Systemic and general disease:
Urticaria, in some cases, may present as a sign of other systemic or general internal diseases such as hormonal disorders (hyperthyroidism), SLE, polycythemia, reticulosis, etc. In a certain variety of malignancies (cancer), urticaria may present as a precursor.
Idiopathic cause:
No list of causation is complete without adding a paragraph of 'Idiopathic' which simply implies causes that are unknown.
Written & Approved by-
Dr. Rajesh Shah
M.D. (Hom.)