Dermatomyositis Homeopathy Treatment and Its Homeopathic Medicine 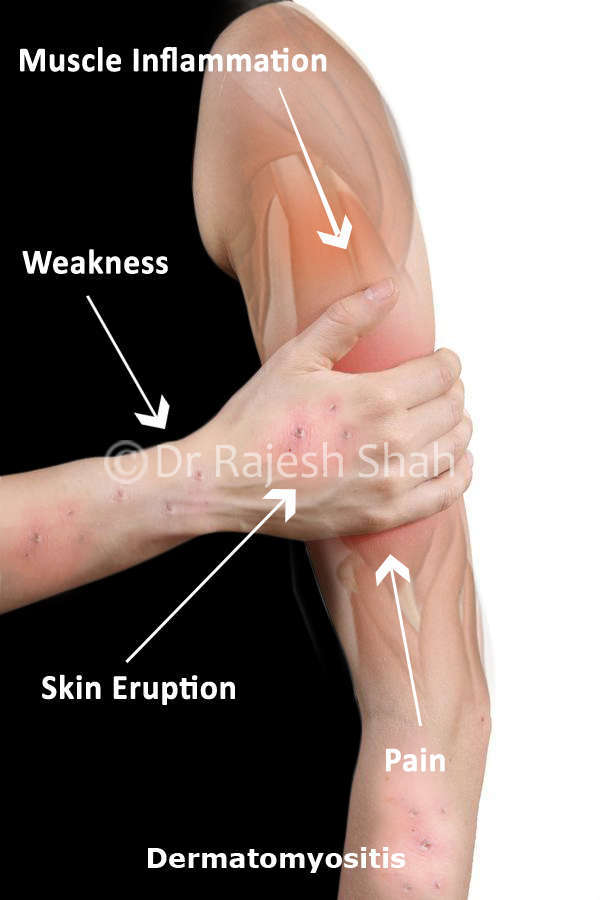
Introduction
Dermatomyositis is a complex disease. To understand in simple language, Dermatomyositis means inflammation of skin and muscles. It is a disease of the connective tissues, the tissues that connect the joints and cartilages. Dermato (=skin)-myo (=muscles)-itis (inflammation), is essentially a disease of the skin tissues and the muscles, but it also can affect joints, lungs, food-pipe as well as the heart.
Dermatomyositis is related to another similar disease called Polymyositis, where, as the name suggests, multiple muscles are inflamed. Both of them may have similar presentation.
Dermatomyositis is an auto-immune, chronic disease which tends to progress over the period of time. Dermatomyositis calls for integrative treatment, that is, judicious use of the conventional medicine combined with homeopathy. The major symptoms are skin rashes preceded over with painful muscular weakness. It is a disease with no permanent cure but the periods of remission can be attained. Treatment can offer to clear the skin rashes and help in regaining the muscular power and strength.
Causes of Dermatomyositis
The exact cause of Dermatomyositis still remains unexplained. Certain genetic, immunological factors and environmental factors may have a relation to the occurrence of the disease.
Genetic predisposition – Dermatomyositis rarely occurs in all familial chain but its relation with the in Human Leukocyte Antigen has been seen.
Immunological imbalance predisposition – Abnormal T–cell activities may be involved. The patient should also look out for the other autoimmune disease in the family which can be highly and strongly prevalent.
Drug-induced – It has been noted that Dermatomyositis has relation with the history of intake of some drugs:
- Penicillamine
- Anti - Tumor necrosis factor-alfa drugs
- Interferon
- Cyclophosphamide
Age and gender:
Dermatomyositis can occur at any age but its high incidence is seen in two peaks of ages :
In adults –over the age of 50 years
In Children – Between the age of 5 – 15 years
In sex, predominance females lead the number of cases than males
Pathology
The skin and the muscles undergo certain changes as under, in Dermatomyositis:
- Atrophic changes can be seen in the epidermis with vascular interface changes.
- Perivascular lymphocytic infiltration. - Increased dermal mucin.
- Myositis with myofiber necrosis.
- Phagocytosis
- Late myofiber atrophy
- Fatty changes.
Symptoms of Dermatomyositis
Most patients Dermatomyositis have skin rash and muscular pain. The most affected muscles are those close to the center of the body, which are called as proximal muscles. That is the upper arms and the thigh muscles.
The symptoms could be listed as under:
- Itching: The itching could be very severe and may be resistant to treatment
- Erythema
- Eruptions near the margins of eye with swelling
- Scaly scalp with diffuse hair loss.
- The muscular weakness with tenderness and severe stiffness in the body.
- Muscles weakness, leading to paralysis of certain group of muscles
- Reduced mobility
- Fever
- Joint pain (Arthralgia)
- Weight loss
Complications of Dermatomyositis
Over the period of time, Dermatomyositis could lead to some internal diseases and symptoms such as:
- Difficulty in talking and inability to communicate
- Conditions in which heart is enlarged and cannot pump blood efficiently (dilated cardiomyopathy)
- Lung involvement due to muscle weakness of muscles of the chest.
- Calcium deposition under the skin causing permanent shortening of muscles, tendons, and/or ligaments of joints.
- Cancers
- Mechanic hands – Rough and cracked skin at the tips of fingers
Dermatomyositis in children (Juvenile Dermatomyositis)
Dermatomyositis, unfortunately, can affect even children. And, at times, it could be very severe in children with the affections of veins and arteries. Affecting primarily the skin and muscle, causing symmetric proximal weakness and skin rash. From the adult form of dermatomyositis, it differs by the presence of vasculitis of the small blood vessels, which can involve the gastrointestinal tract and myocardium, besides skin and muscle.
Juvenile dermatomyositis is not associated with the development of malignancies, unlike adult dermatomyositis.
Prognosis is related to the degree of vasculitis. The overall prognosis for survival is improved following better use of corticosteroid.
It is one of the most common pediatric inflammatory myopathies.
Bimodal age distribution - (ages 5–9 yr and 10–14 yr)
Incidence - 0.5/100,000
Symptoms include:-
Symmetrical and progressive proximal muscle weakness
– Calcinosis.
Scaly and erythematous dermatitis over the dorsum of the hands with Nonpalpable macular rashes. Heliotrope is often associated with periorbital edema and telangiectasias of the upper eyelids.
Raising a child at times can be difficult when dealing with kids who suffer from these ailments. It requires great patience and understanding. Families should learn to adapt to their child’s illness and grow with their experiences.
Take good care of emotional needs of the child. Talk regularly with all members of the family, communicating openly relieves the stress There is no need to be overprotective. Encourage child it is best to maintain a balance. The discipline of your child should not change with the illness.
It is important that your child get back into a normal routine as soon possible.
Future of the disease is variable depending on the severity of the spread of the disease. It takes around 2 years of time minimum to treat the complications of the active flare-up of the disease. Once completely it is resolved reoccurrence changes seems to very less.
How to Diagnose Dermatomyositis?
A good clinician who has experience in treating such collagen diseases could suspect dermatomyositis when the patient presents with inflamed skin, muscles and muscular weakness. If you suffer from the above-mentioned signs and symptoms, your doctor may suggest you following tests to confirm the diagnosis of dermatomyositis:
- Blood Tests: Blood tests detect the levels of certain enzymes which are increased when the muscle is damaged. These include enzymes, such as creatine kinase (CK) and aldolase. The blood test also detects specific antibodies that are produced by the body which damage its own muscle cells. These antibodies are produced by the body as a part of the disease process. Different levels and types of antibodies detected in the blood help to determine the mode of treatment and specific medications to be administered to the patient.
- Electromyography (EMG): This test helps to assess the health of muscles and nerve cells that control their actions and functions. The changes detected by this test confirm the muscle disease as well as the extent of damage to different muscles of the body. Electrical activity in different muscles.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): An MRI of the muscles will assess the inflammation and changes caused by the disease over a large portion of the muscle.
- Skin or muscle biopsy: This test helps to confirm the diagnosis as well as rule out other similar disorders such as lupus and etc. A small piece of your skin or muscle is removed and sent to for laboratory for analysis.
Treatment of Dermatomyositis
Conventional treatment
Conventional treatment promises symptomatic relief but no cure for the disease. Your doctor may prescribe corticosteroids and certain drugs that suppress the immune system such as prednisone, azathioprine and methotrexate. Cyclosporine A, cyclophosphamide, and tacrolimus are also some immune suppressants that your doctor may prescribe. Topical corticosteroids are prescribed for skin rashes.
Surgery
Surgery may be required for patients with calcium deposits to control nerve pain caused by them and recurrent infections.
Supportive Treatment
It is crucial to prevent muscle atrophy in patients with dermatomyositis. Regular physiotherapy helps to improve the strength of muscles and prevent muscle atrophy. It increases the range of motion of the affected muscles. Patients are advised to apply high protection sunscreen and protective clothing to take care of the skin rashes. Bed rest is highly advised for those patients having severely inflamed muscles.
Diet:
Patients are recommended a well-balanced diet is useful. Those who suffer from severe muscle damage and inflammation are advised to take a high-protein diet. The extra protein balances the loss and helps regain muscle mass and strength.
Patients having difficulty in eating should have food early and avoid meals just before bedtime.
Physical Therapy: It is highly recommended to maintain physical activity to the best possible limits. In active phases, vigorous physical training can be avoided. A rehabilitative exercise regimen maintains the patient’s range of motion and prevents extensive muscle damage.
Homeopathic treatment for Dermatomyositis
Homeopathy has a significant role to play in the treatment of Dermatomyositis. Homeopathy is known to have efficacy for a range of immunologically mediated diseases such as dermatomyositis, rheumatoid arthritis, polymyositis, etc. Dermatomyositis is one disease where you need to be treated with an integration of homeopathy with the conventional medicines, to achieve best control and relief.
Homeopathy helps to control the underlying disease process in dermatomyositis, as well as giving relief in the symptoms such as painfulness of muscles, weakness, fatigue and skin rash. It also helps to reduce dependency on immunosuppressive medicines such as corticosteroids or cortisone.
At Life Force, we have treated several cases of Dermatomyositis with encouraging results. Strongly recommended.
Case studies of Dermatomyositis: Case 1, Case 2,
Related Condition:- Polymyositis
Written & Approved by-
Dr. Rajesh Shah
M.D. (Hom.)