Onychomycosis (Nail Fungus) Homeopathy Treatment and Its Homeopathic Medicine
Onychomycosis (onycho means nails and mycosis means fungal infection) is a fungal infection of the fingernails or toenails. The actual infection is of the bed of the nail and of the plate under the surface of the nail. Onychomycosis is also known as Dermatophytic onychomycosis, Ringworm of the nail, and Tinea unguium.
Prevalence:
This condition may affect toenails or fingernails, but toenail infections are prevalent. The prevalence of onychomycosis is about 6-8% in the adult population.
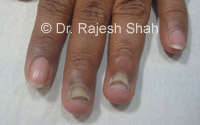
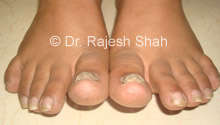
causes:
Here are some factors that contribute to the development of onychomycosis:
1)Dermatophyte Infection: The majority of onychomycosis cases are caused by dermatophyte fungi, such as Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, and Epidermophyton floccosum. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments and can invade the nails through small cuts or separations between the nail and nail bed.
2)Yeasts and Molds: While dermatophytes are the primary culprits, yeasts (such as Candida species) and molds can also cause nail infections. These infections are less common but may occur in certain individuals, especially those with weakened immune systems.
3)Warm and Moist Environments: Fungi thrive in warm and moist conditions. Wearing tight or non-breathable shoes for extended periods, walking barefoot in communal areas like swimming pools and gym showers, and keeping the feet damp can create an environment conducive to fungal growth.
4)Trauma to the Nail: Injuries to the nail or surrounding skin, such as cuts, bruises, or ingrown toenails, can create entry points for fungi to invade the nail bed.
5)Poor Foot Hygiene: Inadequate foot hygiene, such as not keeping the feet clean and dry, can contribute to the development of onychomycosis.
6)Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems, whether due to medical conditions (e.g., diabetes, HIV) or medications (e.g., immunosuppressive drugs), are at an increased risk of developing fungal infections, including onychomycosis.
7)Age and Genetics: The risk of onychomycosis tends to increase with age, and there may be a genetic predisposition that makes some individuals more susceptible to fungal infections.
8)Chronic Diseases: Certain chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, and psoriasis, immune deficiency disease increase the risk of onychomycosis. A history of athlete's foot and excess perspiration are also risk factors.
Symptoms:
The specific signs and symptoms may vary depending on the type of fungus causing the infection and the severity of the condition. Here are common symptoms associated with onychomycosis:
1)Changes in Nail Appearance:
Discolouration: The affected nail may become discoloured, typically developing a yellowish or brownish hue. In some cases, the nail may turn white.
Thickening: The nail may thicken and become more brittle. As the infection progresses, the thickness of the nail can increase significantly.
2) Texture Changes:
Brittleness: Infected nails often become brittle and crumbly, making them more prone to breakage.
Roughness: The surface of the nail may become rough or irregular.
3) Shape Alterations:
Distorted Shape: The infected nail may lose its normal shape and become distorted. This can include changes in curvature and an irregular outline.
4) Separation from Nail Bed:
Onycholysis: The infected nail may separate from the nail bed. This separation can create a gap between the nail and the underlying skin, and debris may accumulate in this space.
5)Pain and Discomfort: Onychomycosis can cause pain or discomfort, especially when pressure is applied to the affected nail, such as during walking or wearing shoes.
6) Odor:
Unpleasant Odor: In some cases, onychomycosis may be associated with a foul odour, particularly when the infection is advanced.
7) Spread to Surrounding Skin:
Skin Involvement: Fungal infection may extend to the surrounding skin, leading to symptoms such as redness, itching, and peeling.
It's important to note that onychomycosis can progress slowly, and some individuals may not experience noticeable symptoms in the early stages. As the infection advances, the symptoms become more apparent.
Diagnosis:
Onychomycosis can be identified by its appearance, microscopy and culture of nail specimens.
Conventional Treatment:
Onychomycosis is very difficult and sometimes impossible to treat, and therapy is often long-term. Therapy consists of topical treatments that are applied directly to the nails, as well as systemic drugs such as griseofulvin and ketoconazole. Oral drugs are not so effective due to the low serum concentration of the drug at the site of the infection.

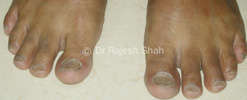
Prevention:
To prevent fungal growth, it is advisable to:
- Keep the feet clean and dry, and washing with soap and water and drying thoroughly
- Keeping the nails cut short and wearing shower shoes whenever walking or showering in public places
- Daily changes of shoes, socks, or hosiery are also helpful
- Excessively tight hose or shoes promote moisture, which in turn, provides a wonderful environment for onychomycotic infections. To prevent this, individuals should wear only socks made of synthetic fibres, which can absorb moisture more quickly than those made of cotton or wool.
- Manicure and pedicure tools should be disinfected after each use
- Nail polish should not be applied to nails that are infected, as this causes the water or moisture that collects under the nail's surface to not evaporate and be trapped.
- Avoid cutting or tearing the skin around the toenails since this may be an entry point for infection
Suggestion about homeopathic treatment:
Homeopathic medicines do not kill the fungus. It enhances the immunity of the body so that the body can fight against the fungus and resist it. Regularly using Homeopathic medicines helps restore the nail and prevent recurrent infections.
After starting homeopathic medicines, natural healing takes place. The nail, if mildly damaged, is repaired. If largely damaged, it falls off and the new nail that comes is healthy and generally can withstand the fungal infection.
Here are a few of homeopathic medicines that may be considered for onychomycosis:
1)Sepia Officinalis: Indicated when nails are discoloured, especially yellow or greenish. Sepia may be considered when there is a tendency for the nails to crack and become brittle.
2)Graphites: Graphites may be recommended when the nails are thick, distorted, and brittle. It is also indicated when there is a tendency for the skin around the nails to be dry and cracked.
3)Silicea: Silicea is suggested when the nails are deformed, thickened, and have a tendency to break easily. It may be considered when there is associated suppuration (formation of pus) around the nails.
4)Sulphur: Sulphur is often prescribed for onychomycosis with symptoms of itching and burning in the affected area. It may be indicated when the nails are thickened and discoloured.
5) Antimonium Crudum: Antimonium Crudum may be considered when there is thickening of the nails, and the skin around the nails is hard and cracked.
It's important to emphasize that homeopathic remedies should be chosen based on a thorough evaluation of the individual's overall health, constitution, and specific symptoms.
Related Conditions:
Written & Approved by-
Dr. Rajesh Shah
M.D. (Hom.)